AI agents like other buzzwords have recently been on the front line. In this article, I explore the various ways we can employ AI Agentic workflow without complexity with and without libraries.
What are AI Agents?
Agents combine language models with tools to create systems that can reason about tasks, decide which tools to use, and iteratively work towards solutions. createAgent() provides a production-ready agent implementation. An LLM Agent runs tools in a loop to achieve a goal. An agent runs until a stop condition is met - i.e., when the model emits a final output or an iteration limit is reached.
Source: https://docs.langchain.com/oss/javascript/langchain/agents
In this post, we’ll look at three libraries and what aproaches they take.
- Microsoft AutoGen
- Google Agent Development Kit
- LangChain Agents
Microsoft AutoGen
pip install -U "autogen-agentchat" "autogen-ext[openai]"# Install AutoGen Studio for no-code GUI
pip install -U "autogenstudio"import asyncio
from autogen_agentchat.agents import AssistantAgent
from autogen_ext.models.openai import OpenAIChatCompletionClient
async def main() -> None:
model_client = OpenAIChatCompletionClient(model="gpt-4.1")
agent = AssistantAgent("assistant", model_client=model_client)
print(await agent.run(task="Say 'Hello World!'"))
await model_client.close()
asyncio.run(main())# First run `npm install -g @playwright/mcp@latest` to install the MCP server.
import asyncio
from autogen_agentchat.agents import AssistantAgent
from autogen_agentchat.ui import Console
from autogen_ext.models.openai import OpenAIChatCompletionClient
from autogen_ext.tools.mcp import McpWorkbench, StdioServerParams
async def main() -> None:
model_client = OpenAIChatCompletionClient(model="gpt-4.1")
server_params = StdioServerParams(
command="npx",
args=[
"@playwright/mcp@latest",
"--headless",
],
)
async with McpWorkbench(server_params) as mcp:
agent = AssistantAgent(
"web_browsing_assistant",
model_client=model_client,
workbench=mcp, # For multiple MCP servers, put them in a list.
model_client_stream=True,
max_tool_iterations=10,
)
await Console(agent.run_stream(task="Find out how many contributors for the microsoft/autogen repository"))
asyncio.run(main())import asyncio
from autogen_agentchat.agents import AssistantAgent
from autogen_agentchat.tools import AgentTool
from autogen_agentchat.ui import Console
from autogen_ext.models.openai import OpenAIChatCompletionClient
async def main() -> None:
model_client = OpenAIChatCompletionClient(model="gpt-4.1")
math_agent = AssistantAgent(
"math_expert",
model_client=model_client,
system_message="You are a math expert.",
description="A math expert assistant.",
model_client_stream=True,
)
math_agent_tool = AgentTool(math_agent, return_value_as_last_message=True)
chemistry_agent = AssistantAgent(
"chemistry_expert",
model_client=model_client,
system_message="You are a chemistry expert.",
description="A chemistry expert assistant.",
model_client_stream=True,
)
chemistry_agent_tool = AgentTool(chemistry_agent, return_value_as_last_message=True)
agent = AssistantAgent(
"assistant",
system_message="You are a general assistant. Use expert tools when needed.",
model_client=model_client,
model_client_stream=True,
tools=[math_agent_tool, chemistry_agent_tool],
max_tool_iterations=10,
)
await Console(agent.run_stream(task="What is the integral of x^2?"))
await Console(agent.run_stream(task="What is the molecular weight of water?"))
asyncio.run(main())# Run AutoGen Studio on http://localhost:8080
autogenstudio ui --port 8080 --appdir ./my-appGoogle Agent Development Kit
For initiating a google agent project, we need a folder structure:
mkdir -p my-agent/ && \
touch my-agent/agent.ts \
my-agent/package.json \
my-agent/.envimport {FunctionTool, LlmAgent} from '@google/adk';
import {z} from 'zod';
/* Mock tool implementation */
const getCurrentTime = new FunctionTool({
name: 'get_current_time',
description: 'Returns the current time in a specified city.',
parameters: z.object({
city: z.string().describe("The name of the city for which to retrieve the current time."),
}),
execute: ({city}) => {
return {status: 'success', report: `The current time in ${city} is 10:30 AM`};
},
});
export const rootAgent = new LlmAgent({
name: 'hello_time_agent',
model: 'gemini-2.5-flash',
description: 'Tells the current time in a specified city.',
instruction: `You are a helpful assistant that tells the current time in a city.
Use the 'getCurrentTime' tool for this purpose.`,
tools: [getCurrentTime],
});cd my-agent/
# initialize a project with default values
npm init --yes
# configure TypeScript
npm install -D typescript
npx tsc --init
# install ADK libraries
npm install @google/adk
npm install @google/adk-devtools{
"name": "my-agent",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "My ADK Agent",
"main": "agent.ts",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"devDependencies": {
"typescript": "^5.9.3"
},
"dependencies": {
"@google/adk": "^0.2.0",
"@google/adk-devtools": "^0.2.0"
}
} // set to false to allow CommonJS module syntax:
"verbatimModuleSyntax": false,npx tscnpx @google/adk-devtools run agent.tsnpx @google/adk-devtools webMulti-agent
import 'dotenv/config';
import { FunctionTool, LlmAgent } from '@google/adk';
import { z } from 'zod';
const getWeather = new FunctionTool({
name: 'get_weather',
description: 'Retrieves the current weather report for a specified city.',
parameters: z.object({
city: z.string().describe('The name of the city for which to retrieve the weather report.'),
}),
execute: ({ city }) => {
if (city.toLowerCase() === 'new york') {
return {
status: 'success',
report:
'The weather in New York is sunny with a temperature of 25 degrees Celsius (77 degrees Fahrenheit).',
};
} else {
return {
status: 'error',
error_message: `Weather information for '${city}' is not available.`,
};
}
},
});
const getCurrentTime = new FunctionTool({
name: 'get_current_time',
description: 'Returns the current time in a specified city.',
parameters: z.object({
city: z.string().describe("The name of the city for which to retrieve the current time."),
}),
execute: ({ city }) => {
let tz_identifier: string;
if (city.toLowerCase() === 'new york') {
tz_identifier = 'America/New_York';
} else {
return {
status: 'error',
error_message: `Sorry, I don't have timezone information for ${city}.`,
};
}
const now = new Date();
const report = `The current time in ${city} is ${now.toLocaleString('en-US', { timeZone: tz_identifier })}`;
return { status: 'success', report: report };
},
});
export const rootAgent = new LlmAgent({
name: 'weather_time_agent',
model: 'gemini-2.5-flash',
description: 'Agent to answer questions about the time and weather in a city.',
instruction: 'You are a helpful agent who can answer user questions about the time and weather in a city.',
tools: [getWeather, getCurrentTime],
});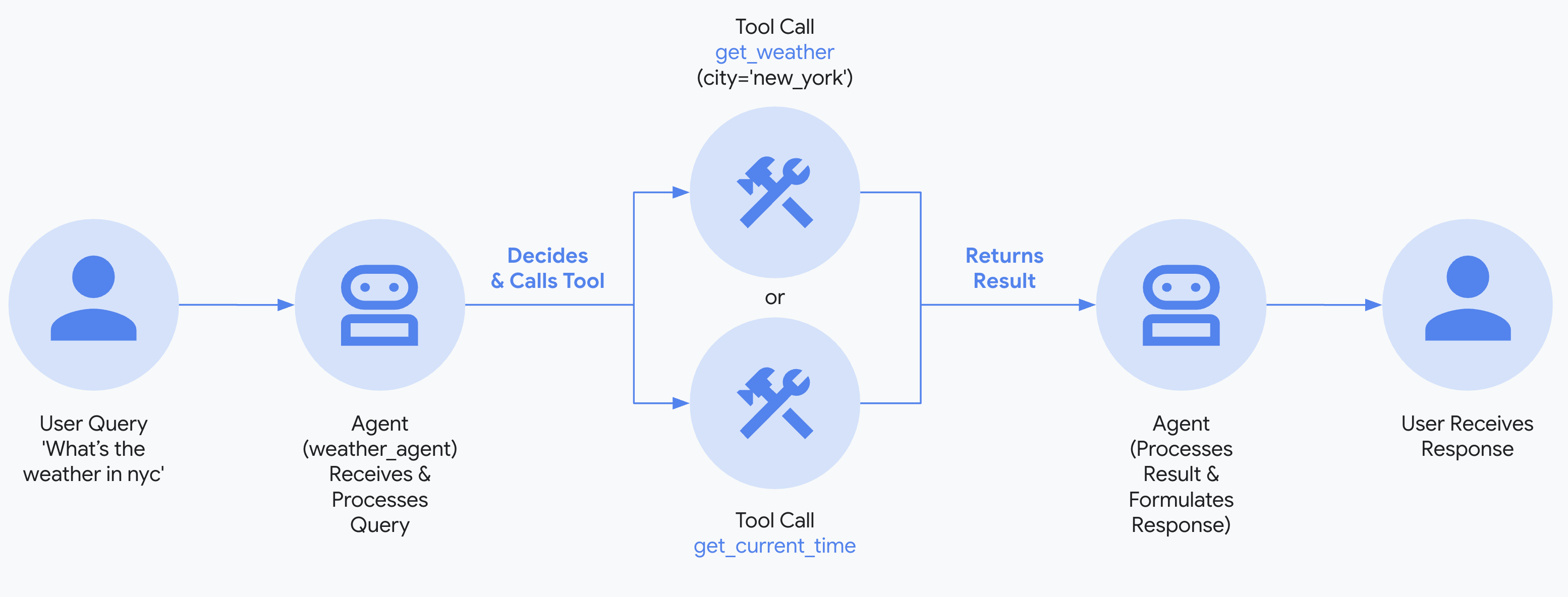 Source: https://google.github.io/adk-docs/get-started/quickstart/#env_1
Source: https://google.github.io/adk-docs/get-started/quickstart/#env_1
LangChain Agents
LangChain provides a graph-based agent runtime using LangGraph. The createAgent() function builds agents that move through nodes (steps) and edges (connections), executing model calls and tools in a ReAct (Reasoning + Acting) loop.
npm install langchain @langchain/openaiBasic Agent
import { createAgent } from "langchain";
const agent = createAgent({
model: "gpt-4o",
tools: [],
systemPrompt: "You are a helpful assistant. Be concise and accurate.",
});
const result = await agent.invoke({
messages: [{ role: "user", content: "What's the capital of France?" }],
});Defining Tools
Tools give agents the ability to take actions. Agents facilitate multiple tool calls in sequence, parallel execution when appropriate, and tool retry logic with error handling.
import * as z from "zod";
import { createAgent, tool } from "langchain";
const search = tool(
({ query }) => `Results for: ${query}`,
{
name: "search",
description: "Search for information",
schema: z.object({
query: z.string().describe("The query to search for"),
}),
}
);
const getWeather = tool(
({ location }) => `Weather in ${location}: Sunny, 72°F`,
{
name: "get_weather",
description: "Get weather information for a location",
schema: z.object({
location: z.string().describe("The location to get weather for"),
}),
}
);
const agent = createAgent({
model: "gpt-4o",
tools: [search, getWeather],
});
const result = await agent.invoke({
messages: [{ role: "user", content: "What's the weather in San Francisco?" }],
});Dynamic Model Selection with Middleware
Middleware allows you to intercept and modify agent behavior at different stages of execution—useful for dynamic model routing, guardrails, and logging.
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
import { createAgent, createMiddleware } from "langchain";
const basicModel = new ChatOpenAI({ model: "gpt-4o-mini" });
const advancedModel = new ChatOpenAI({ model: "gpt-4o" });
const dynamicModelSelection = createMiddleware({
name: "DynamicModelSelection",
wrapModelCall: (request, handler) => {
// Choose model based on conversation complexity
const messageCount = request.messages.length;
return handler({
...request,
model: messageCount > 10 ? advancedModel : basicModel,
});
},
});
const agent = createAgent({
model: "gpt-4o-mini",
tools: [search, getWeather],
middleware: [dynamicModelSelection],
});Structured Output
When you need the agent to return data in a specific format:
import * as z from "zod";
import { createAgent } from "langchain";
const ContactInfo = z.object({
name: z.string(),
email: z.string(),
phone: z.string(),
});
const agent = createAgent({
model: "gpt-4o",
responseFormat: ContactInfo,
});
const result = await agent.invoke({
messages: [
{
role: "user",
content: "Extract contact info from: John Doe, [email protected], (555) 123-4567",
},
],
});
console.log(result.structuredResponse);
// { name: 'John Doe', email: '[email protected]', phone: '(555) 123-4567' }Streaming Responses
For long-running agent tasks, stream intermediate progress:
const stream = await agent.stream(
{
messages: [{
role: "user",
content: "Search for AI news and summarize the findings"
}],
},
{ streamMode: "values" }
);
for await (const chunk of stream) {
const latestMessage = chunk.messages.at(-1);
if (latestMessage?.content) {
console.log(`Agent: ${latestMessage.content}`);
} else if (latestMessage?.tool_calls) {
const toolCallNames = latestMessage.tool_calls.map((tc) => tc.name);
console.log(`Calling tools: ${toolCallNames.join(", ")}`);
}
}Tool Error Handling
Customize how tool errors are handled using middleware:
import { createAgent, createMiddleware, ToolMessage } from "langchain";
const handleToolErrors = createMiddleware({
name: "HandleToolErrors",
wrapToolCall: async (request, handler) => {
try {
return await handler(request);
} catch (error) {
return new ToolMessage({
content: `Tool error: Please check your input and try again. (${error})`,
tool_call_id: request.toolCall.id!,
});
}
},
});
const agent = createAgent({
model: "gpt-4o",
tools: [search, getWeather],
middleware: [handleToolErrors],
});Source: https://docs.langchain.com/oss/javascript/langchain/agents
Summary
Each agent development kit has similar approaches with minor variations. It is nice to have a variety of options to choose from.